UFS (Universal Flash Storage) chips are a high-performance storage solution widely used in smartphones, tablets, embedded devices, and other applications. The FT (Functional Test) aging test fixture is a specialized device used for functional and aging testing of UFS chips, aimed at verifying the stability and reliability of the chips during long-term use.

Product Introduction
The main functions of the UFS chip FT aging test fixture include:
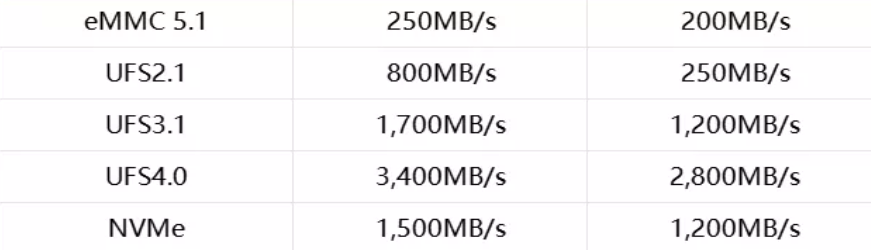
- Functional Testing: Verifying the basic read and write functions of the UFS chip to ensure it operates normally under various conditions. The UFS 4.0 standard was developed for mobile devices that require high performance and low power consumption. It is a high-performance interface that brings significant improvements in bandwidth and data protection. The high-speed serial interface and optimized protocol can significantly enhance throughput and mobile system performance. UFS 4.0 utilizes the M-PHY 5.0 specification and UniPro 2.0 specification, doubling the UFS interface bandwidth and supporting read and write traffic of up to 4.2GB/s, with continuous read and write speeds reaching 3400MB/s.
- Aging Testing: Simulating actual usage conditions through prolonged high-load operation to detect the stability and reliability of the chip under high temperature and high load.
- Data Integrity Testing: Ensuring the integrity and consistency of data during long-term read and write operations.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating key performance indicators of the UFS chip, including read and write speeds and random access performance.
- Temperature and Voltage Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of the chip’s temperature and voltage changes during testing to ensure operation within safe limits.
Testing Key Points
When conducting FT aging tests on UFS chips, the following key points should be noted:
- Testing Environment: Ensure that the testing environment’s temperature, humidity, and other conditions meet standard requirements to avoid external factors affecting the test results.
- Testing Duration: Aging tests typically require a long duration (from several hours to several days) to ensure the chip’s stability during long-term use.
- Load Conditions: During testing, simulate actual usage scenarios and apply appropriate read and write loads to assess the chip’s performance under high load.
- Data Monitoring: Continuously monitor key parameters such as read and write speeds, error rates, and temperature during testing, and promptly record any anomalies.
- Test Result Analysis: After testing, conduct a detailed analysis of the data to evaluate the chip’s performance and reliability, determining whether it meets design specifications.
- Diverse Testing: In addition to basic functional and performance testing, various testing modes (such as random read/write and sequential read/write) can be employed to comprehensively assess the chip’s performance.

By following these testing protocols, the performance and reliability of UFS chips can be effectively evaluated, providing important insights for subsequent product applications.
发表回复